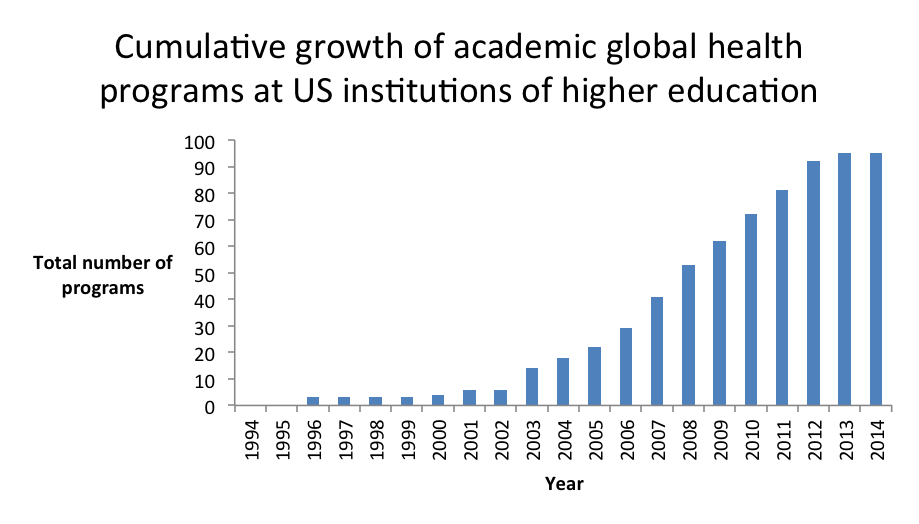
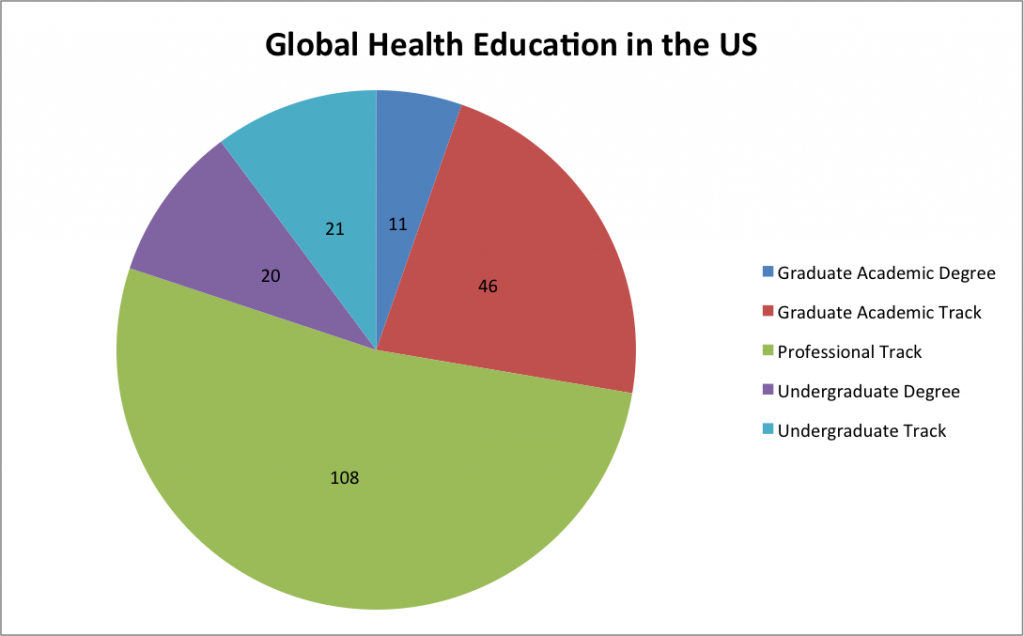
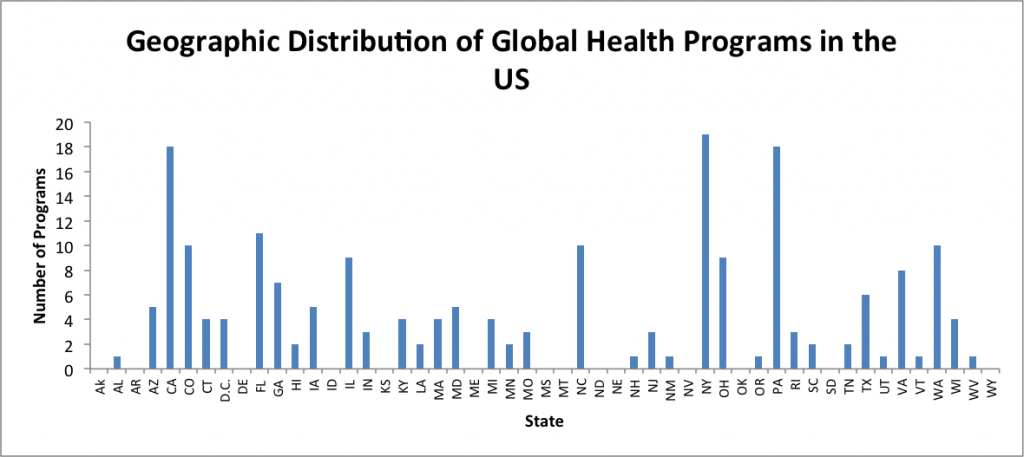
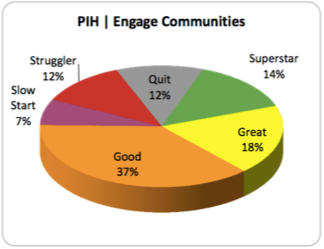
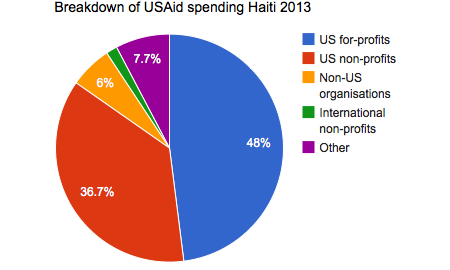
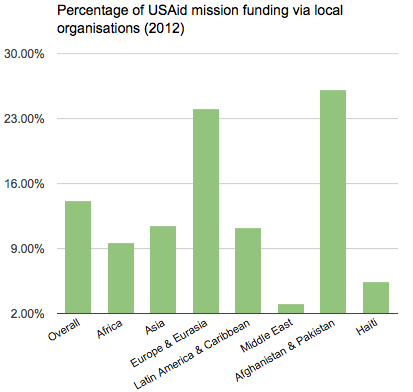
Just finished reading the fantastic article by Elizabeth Tobin Tyler on how we might start to conceptualize and advance a strategy for health as a human right in the United States. It made me realize just how weak our (in the U.S.) legal precedent and political appetite is for positive social and economic rights, including the right to health. The paper reinforced for me the history that the commitment to social and economic rights is, actually, deeply American, but was derailed by the politics of east-west / capitalist-communist posturing of the Cold War. It also gave me some hope that we may be able to begin to move away from a futile top-down, overly litigious, court-driven means of advancing the health as a human right agenda.
The idea advanced in this paper is centered around the potential power of linking health practitioners, lawyers, and community organizers: politicizing health care delivery and baking rights-based advocacy right in to the process of providing services:
“A systemic health and human rights strategy should be built upon interdisciplinary partnerships among health care providers, public health practitioners, lawyers, and community organizers. It should be founded on three principles: bearing witness to human rights violations within the community context; tracking systemic failures through data collection and monitoring; and broad-based legal strategies which include both individual and policy advocacy in a given community.”
Medical-legal partnerships are one way that this type of community-level partnership has been built between these different professional disciplines.
“The medical-legal partnership (MLP) movement in the US exemplifies a community-based health and human rights strategy that implements a legal advocacy and social accountability approach by connecting lawyers, health care providers, and public health practitioners. The MLP model, first established in a safety-net hospital pediatrics department in 1993, now exists in over 500 legal and medical institutions in the US. The model is also being adopted in both Australia and Canada.”
Clearly, MLPs should play a role in a rights-based advocacy strategy in the U.S. But, I wonder how this type of patient-provider-level accountability and advocacy could be used to politicize the act of global health delivery in low income countries? If the goal is to enable MOHs and governments to take on the responsibility for protecting the right to health of their citizens, don’t those citizens need mechanisms to hold those governments accountable for delivering on that duty?
It seems like a movement for the right to health requires both the “supply side” — creating the policy and financing space through foreign aid and “accompaniment” — and the “demand side” — legal recourse for those receiving substandard care or none at all.
Definitely some interesting stuff when considering a country like the U.S., which should have dealt with these issues long ago. But, for nations interested in building the systems of social protection and healthcare delivery to protect citizens’ right to health, ideas such as MLPs should be built in.